When buying a car, choosing between a 3-cylinder engine or a 4-cylinder engine can be a key factor, as each engine has its own unique advantages. 3-cylinder engines are lightweight and fuel-efficient, making them ideal for city driving, while 4-cylinder engines offer more power and smoother performance, making them better suited for long trips and highway driving. In this blog, we’ll break down the differences between these engines, covering fuel efficiency, power output, and best use cases to help you decide which option is best for your driving needs.
4-cylinder vs. 3-cylinder comparison
| feature | four cylinder engine | Three-cylinder engine |
| Power output | Usually the higher power output is due to the extra cylinders. Ideal for large or performance oriented vehicles. | The power is lower and usually sufficient for a compact or economy car. |
| Smoothness | Smoother operation due to balanced power delivery. | The vibration is slightly greater; a balance shaft is required to ensure smoothness. |
| fuel efficiency | Fuel efficiency is good, but slightly lower than a three-cylinder engine due to the extra weight and friction. | Better fuel efficiency due to fewer moving parts and lighter weight. |
| Weight and dimensions | Heavier and larger, it takes up more space in the engine bay. | Lighter and more compact for better use of space. |
| cost | Usually more expensive due to extra parts and complexity. | Usually production and maintenance costs are lower. |
| Application areas | Commonly found in sedans, SUVs, and performance cars. | Perfect for compact, fuel-efficient city cars. |
What is a 4-cylinder engine?
An inline 4-cylinder engine is an engine with four cylinders arranged at 90 degrees. The 4-cylinder engine design is a normal-sized design commonly found in automotive engines. This engine typically consumes less fuel than an engine with larger cylinders, such as an eight-cylinder or six-cylinder engine. In general, all engines convert chemical energy in the fuel into heat; rather than converting heat energy into mechanical work.
Components of a four-cylinder engine
- Cylinders and Pistons: The main component that allows the combustion of a gas mixture to generate electricity.
- Crankshaft: It is the part that rotates the crank and converts the radial and axial graphic motion of the piston into the angular motion required to rotate the wheel.
- Camshaft: Operates the timing of the engine’s intake and exhaust valves.
- Fuel injector: Inject the necessary fuel into the appropriate cylinder.
- spark plug: They are responsible for burning the fuel-air mixture.
- Exhaust system: Helps remove gases produced during combustion from inside the engine to the surrounding atmosphere.
How a 4-cylinder engine works
- Intake: The stage during which the piston moves freely in a chamber filled with air-fuel mixture due to the opening of the intake valve.
- compression: After the intake phase ends, the stroke is entered, the intake valve closes, and the piston in the cylinder compresses the stored gaseous fuel.
- combustion: Enclosed in the upper part of the cylinder, there is a mixture of air and fuel, in which a spark plug is placed to initiate combustion and push down the cylinder.
- exhaust: This involves opening the exhaust valve portion to allow the gas filling the cylinder head cavity to escape.
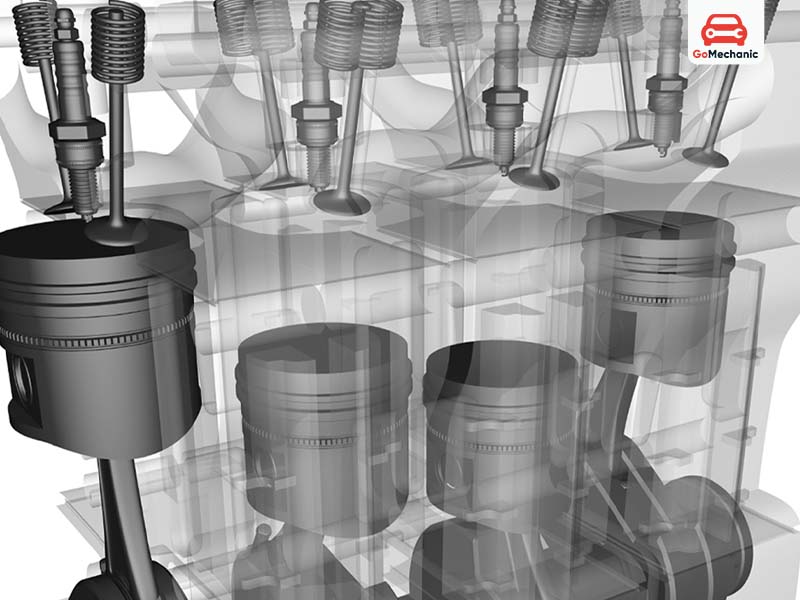

These four stages occur in each cylinder in a fixed sequence, which helps maintain uninterrupted power. Most 4-cylinder engines use an inline or in-line engine layout, which means the cylinders are located in a single row rather than being placed in separate groups or rows
Advantages and disadvantages of 4-cylinder engines
| advantage | shortcoming |
| Fuel efficient | Less powerful than larger engines |
| Smooth operation | Slightly lower fuel consumption than three-cylinder |
| Compact and lightweight | Not suitable for high performance needs |
| lower emissions | Will vibrate under heavy load |
| Suitable for various car models | Heavier than 3-cylinder engine |
Why would you choose a 4-cylinder engine?
Individuals commuting over long distances and busy roads who need more power to maneuver or maintain higher speeds over longer distances will benefit more from the power and smoothness of a 4-cylinder diesel engine.
What is a three-cylinder engine?
The phrase “inline three-cylinder engine” describes a three-cylinder piston engine configuration in which all cylinders are located in the same crankcase. As we all know, this type of engine is not as widely used as the more popular four-stroke engines, but three-cylinder engines can be found in a range of vehicles, including cars and motorcycles. Their crankshaft angle is at 120 degrees. Therefore, their emission intervals have equal distribution.

Components of a three-cylinder engine
- cylinder: The cylinder and piston assembly is the basic unit for the combustion of a combustible mixture to produce work.
- Crankshaft: It is the component that converts the linear motion of the vertical piston into the rotational motion of the connecting wheel in the crankcase.
- Camshaft: It is the part that operates the intake and exhaust valves in the engine to open and close.
- fuel injector – Injectors introduce the necessary energy into each master cylinder.
- spark plug: Automotive spark plugs are the grounded component of any engine’s ignition system and are used in the cyclic combustion process of any gas or steam, allowing a high-voltage electric spark to ignite the gas within the cylinder.
- Exhaust system: This system directs combustion by-products produced by the internal engine machinery through various combustion processes away from the vehicle.
How a three-cylinder engine works
- Intake: The intake valve of the cylinder opens, using the Venturi effect to draw the air-fuel mixture into the cylinder.
- compression: The intake valve closes and the piston moves upward to compress the mixture.
- combustion: The spark plug ignites a compressed mixture of air and gas, causing an explosion that forces the piston downward, thereby producing work.
- exhaust: The cylinder’s exhaust valve opens, allowing any combustion gases that may be present to leave the cylinder.
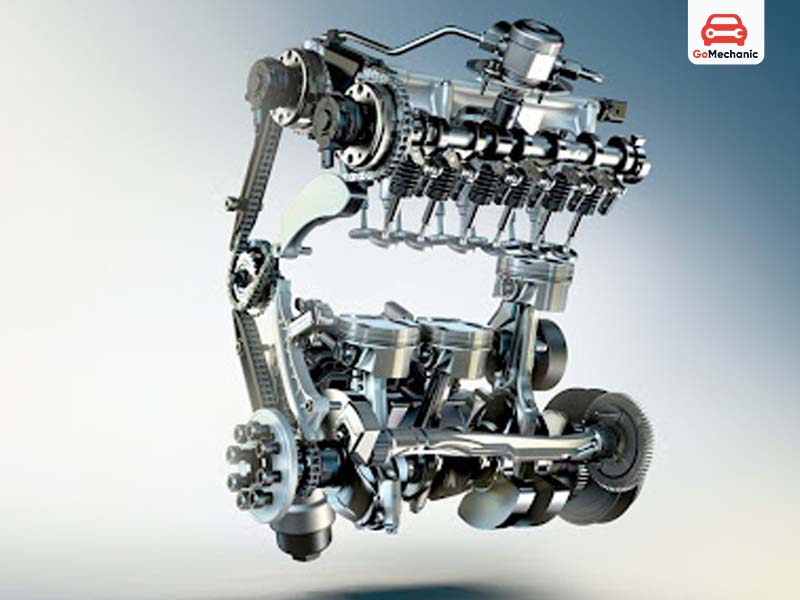

Every component and every cylinder in these engines undergoes a process that consists of, occurs and coordinates multiple stages. Three-cylinder engines will experience more torsional vibration than four-cylinder engines because they have one less cylinder, but they will likely be more compact and efficient. Most 3-cylinder engines are also designed as in-line, with the cylinders arranged in a single bank.
Advantages and disadvantages of three-cylinder engines
| advantage | shortcoming |
| Better fuel efficiency | lower power output |
| Lightweight and compact | More vibration, poor smoothness |
| lower emissions | Limited to small, city-focused cars |
| High cost performance | Not suitable for high performance needs |
Reasons for choosing a three-cylinder engine?
It’s suitable for shorter distances and is best suited for those who are more focused on fuel efficiency than performance. Vehicles with three-cylinder engines are cheaper and therefore suitable for rational people.
Preferred 4 and 3 cylinder cars in India

Popular 4-cylinder engine cars
- Hyundai Grand i10
- Maruti Suzuki Baleno
Popular three-cylinder engine cars
Check it out – The 10 best-selling cars in the third quarter of 2024
Which engine cylinder is best?
Three-cylinder engines are best for those who value fuel efficiency, economy and environmentally friendly design, such as city drivers and those on a budget. However, 4-cylinder engines are suitable for situations where higher engine performance and fast acceleration are required, especially when driving on the highway.
It’s important to the customer’s driving experience to understand that the decision to choose a three-cylinder engine over a four-cylinder engine also affects the way the driver handles the car. The choice between a three-cylinder engine and a four-cylinder engine therefore depends strictly on individual needs and driving considerations.
Also Read- 3-Cylinder Engines vs. 4-Cylinder Engines: Performance, Efficiency, Maintenance











Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.