
Ever wonder how all car engine parts work? Technology is getting more and more advanced. Likewise, the engine works as well. SOHC and DOHC are terms often used when talking about internal combustion engine performance, efficiency and design; however, what people may not know is that both are related to the layout of the engine’s camshaft. The basic difference lies in the construction and performance of this type of engine design.
This blog will provide a comprehensive overview SOHC and DOHC engines Includes their functions, advantages, disadvantages, complete forms of SOHC vs. DOHC, differences between SOHC and DOHC, and other related concepts such as VVT, reliability, fuel economy, and maintenance. So, after reading the entire article, you can easily understand which one is best for you.
Also read: Power Gasoline vs. Regular Gasoline: Learn the Best Fuel Options for Your Engine
What does camshaft mean?
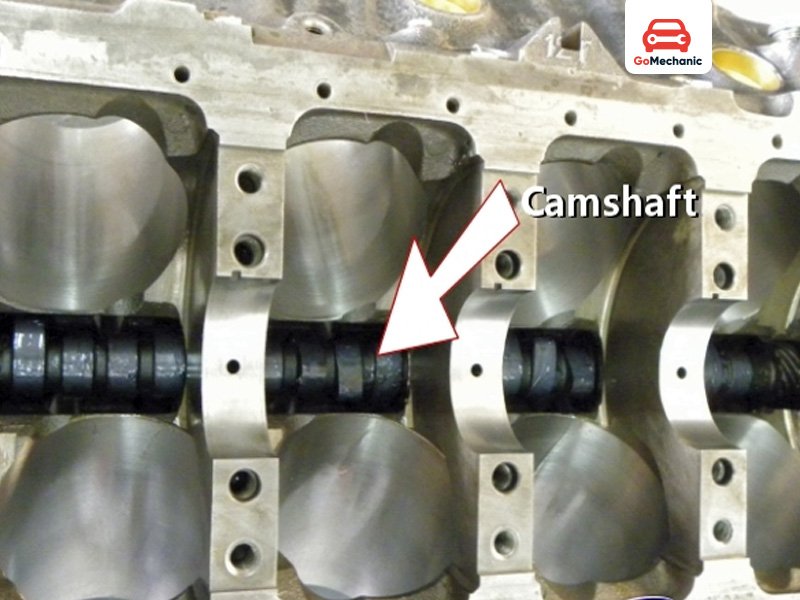
The camshaft is an important component of an internal combustion engine because it opens and closes the engine’s intake and exhaust valves. When open, air-fuel mixture enters the cylinder while exhaust gases exit the engine. The crankshaft drives the camshaft. The camshaft consists of a series of cams or lobes that push the valves and open and close them according to set timing.
In-engine function of camshaft
- Valve timing: The specific time or period at which each valve opens or closes from any other part of the camshaft will therefore affect the engine’s power and economy levels.
- Valve lift: The cam will control how high each valve lifts, thereby controlling how much air and fuel is brought into the engine.
- Engine performance: This determines how the engine adjusts to the camshaft design to achieve specific performance specifications such as power, fuel economy and smoothness.
- Exhaust and intake control: It also ensures the correct timing of the exhaust gases and the close intake of the fresh air-fuel mixture within the engine cylinders.
Related: How a car engine works
How camshafts and valves work
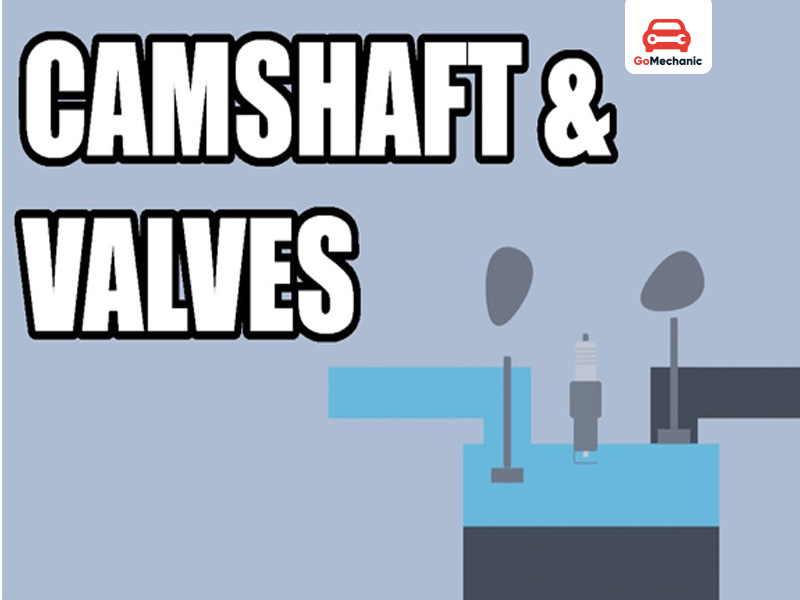
The valve opens via the camshaft. Therefore, the air-fuel mixture enters the cylinder, or the exhaust gases leave the cylinder through the camshaft. The camshaft rotates and then pushes on a lobe or push rod on the rocker arm, which opens and closes the timing valve.
What are the different classifications of camshaft positions?
Categories of camshaft position:
- The term “overhead valve” refers to an engine that has a camshaft within its engine block that uses pushrods and rocker arms to actuate the valves.
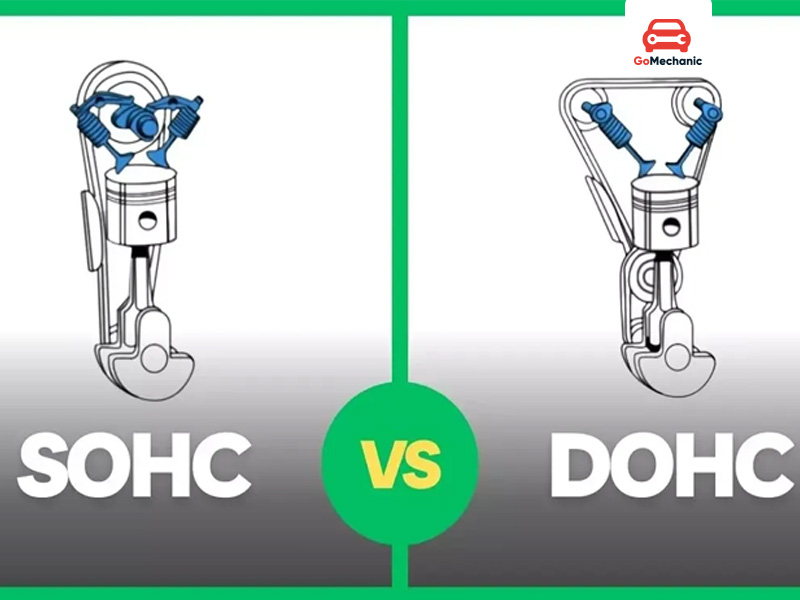
- A single overhead camshaft (SOHC) has the camshaft located at the top of the engine for the functions of the intake and exhaust valves.
- Dual overhead camshafts (DOHC) are two camshafts located on top of the engine inside the engine block, used to independently control the intake and exhaust valves.
Single overhead camshaft (SOHC) engine
In its full form, SOHC is a single overhead camshaft engine consisting of a camshaft mounted in the upper part of the engine block and operating the intake and exhaust valves through rocker arms, pushrods or any other mechanism. These types of engines are usually very simple, cheap, and require fewer parts to maintain. SOHC engines have a single camshaft located in the upper part of the engine block. The camshaft that operates the intake and exhaust valves uses rocker arms or similar components. This type of SOHC engine is more commonly used in small economy cars.
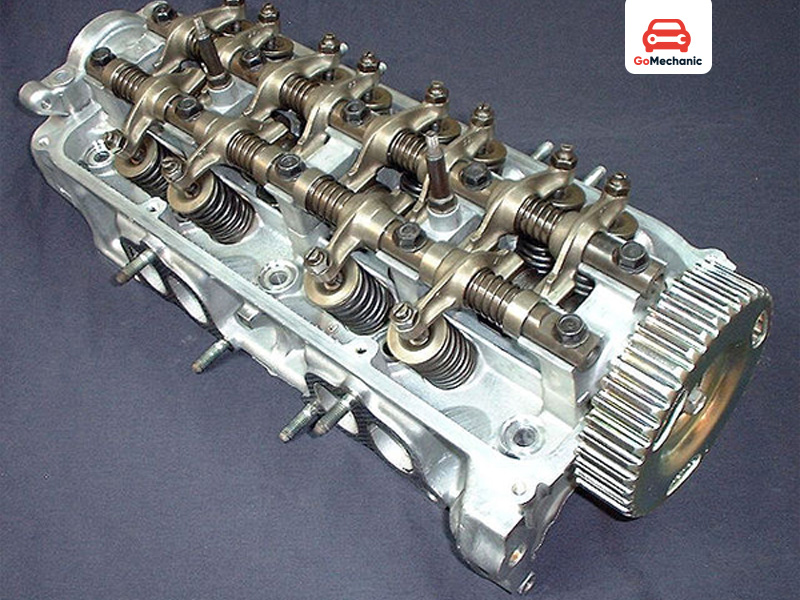
How SOHC works:
Typically, a typical SOHC engine contains a camshaft under the cylinder head that controls the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves. The rotation of the camshaft is driven by a timing belt or chain; the latter is connected to the crankshaft. As the camshaft rotates, individual lobe cams push or actuate rocker arms, opening and closing the valves at specific intervals during engine operation. This simple configuration will enable efficient engine operation at lower manufacturing costs, although it is well suited for high-performance applications due to limited flexibility in valve control.
Advantages of SOHC
- Cost-Effectiveness: Fewer parts make engine production and maintenance simpler and less expensive.
- Simplicity: Fewer moving parts compared to DOHC engines, which can lead to better reliability in some situations.
- Compact: A more compact design can make the engine lighter.
Disadvantages of SOHC
- Performance Limitations: Because only one camshaft drives the intake and exhaust valves, SOHC engines generally do not produce similar performance characteristics compared to DOHC engines.
- Limitations of Valve Control: There are limits to optimizing intake and exhaust valve timing to maximize efficiency or performance.
Double overhead camshaft (DOHC) engine
DOHC stands for Dual Overhead Camshaft. Engines have two camshafts in the overhead position, such as a dual overhead camshaft or DOHC engine. One camshaft controls the intake valve and the other camshaft controls the exhaust valve. As a result, it provides more precise valve timing and engine performance. DOHC engines have two camshafts in the upper part of the engine, one camshaft operates the intake valve and the other camshaft controls the exhaust valve. This allows for better engine and valve timing control.
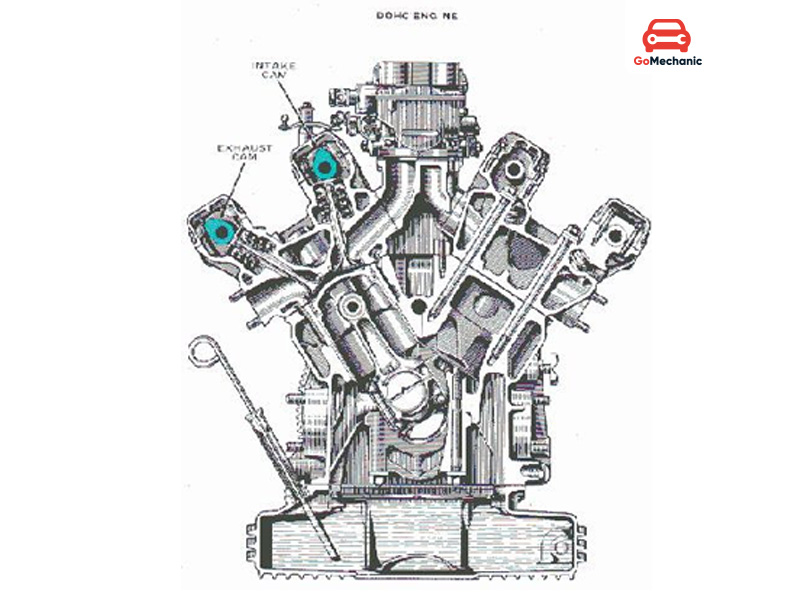
How DOHC works:
In a DOHC engine, each cylinder head has two camshafts, one for the intake valve and one for the exhaust valve. That is, control of valve timing and movement is closer than in a single-camshaft engine. This breathing also significantly enhances breathability both inside and outside the combustion chamber. A cylinder can have four valves, two for exhaust purposes and two for intake. So, in addition to better performance, one can also expect higher output and greater efficiency from this engine in terms of fuel and power. More expensive and heavier than SOHC engines.

Advantages of double overhead camshafts
- Performance improvements: A dual-camshaft arrangement helps improve engine performance due to better control of intake and exhaust valve timing and lift.
- Higher RPM Capability: Typically, DOHC engines can run at higher revolutions per minute (RPM), which is a critical factor in high-performance cars and high-speed engines.
- Better valve timing: The independent working of the intake and exhaust valves allows the engine to be fine-tuned to optimize power and fuel consumption.
Disadvantages of DOHC
- Complexity: More components typically make the design of a single engine more complex, which can result in higher repair costs.
- Weight: The addition of accessories results in the overall weight of the engine being heavier than would be the case with other engine designs.
- Cost: They are often expensive to produce and maintain due to the added complexity and parts used.
DOHC vs. SOHC Engines: A Detailed Comparison
The difference between SOHC and DOHC can be explained using this table
| feature | SOHC | dihydro HC |
| camshaft | 1 (single) | 2 (double) |
| valve control | Easier valve control | Independent control of intake and exhaust valves |
| Performance | Average performance | High performance, optimized valve timing |
| complex | Simple, fewer components | Complex, more parts need to be managed |
| cost | lower cost | higher cost |
| fuel efficiency | ease | Higher, especially when using VVT |
| reliability | More reliable in some cases | In some cases, more parts may reduce reliability |
| maintain | easier and cheaper | More expensive and complex |
| weight | lighter | heavier |
What is VVT?
From a modern engine perspective, variable valve actuation (VVA) can time the opening and closing of engine valves according to speed and load specifications, allowing the engine to produce the best combination of performance and fuel efficiency.
Also read: Four-cylinder engine vs. three-cylinder engine – which one is right for you?

Characteristics of VVT in DOHC engines
- BETTER POWER DELIVERY: Variable valve timing refers to dynamically controlling the effective valve timing events of the intake and exhaust valves, resulting in smooth power delivery over a wider engine speed range.
- IMPROVED FUEL EFFICIENCY: VVT valve timing optimization improves combustion, resulting in greater fuel economy.
- Reduced Emissions: VVT reduces exhaust emissions due to more efficient combustion.
VTEC DOHC and SOHC
It is an abbreviation for Variable Timing and Hydraulic Control of Normal Valve Lift by an electronic system. In fact, this is a system conceived and developed by Honda in its earliest stages to combine fuel efficiency at low speeds with increased revolutions per minute (RPM) at high speeds to improve power.
VTEC DOHC: For variable valve timing control of both camshafts. It produces powerful power at high rpm and high efficiency.
VTEC SOHC: It is equipped with a single camshaft variable valve timing system, and although it provides power performance availability, it does not directly talk about the superiority of DOHC.
SOHC vs. DOHC reliability
It is important to understand the difference in reliability between SOHC and DOHC. Since SOHCs have simpler designs with fewer moving parts and simpler timing systems, they are generally better in terms of reliability. The fewer components there are, the less chance of mechanical failure. However, DOHC engines have more parts, so the potential for long-term wear and tear increases. However, enhanced control can be achieved through valves, which, if managed properly, can make the engine last longer.
Further reading: Engine Oil Grades Explained | Know Your Car’s Engine Oil
SOHC vs. DOHC fuel efficiency
When considering fuel economy, DOHC engines have an advantage because independent operation, especially with the help of the VVT system, results in optimal combustion and fair fuel economy over a wider range of engine speeds. Nonetheless, SOHC is still very efficient for everyday or light-duty applications such as compact cars or motorcycles.

Also read: Choosing the best engine oil for your car: detailed instructions
in conclusion
Now that we’ve finally delved into the DOHC vs. SOHC engine dichotomy, the decision is now up to you, really. What do you value most in a vehicle: fuel efficiency, maximum performance, or a perfect combination of both? What you learn about camshafts and these different engine types, in addition to advanced systems like variable valve timing (VVT), will be a great way to absorb knowledge while also helping you make informed and informed decisions. Remember, choosing the right engine involves more than just researching the specs; It digs deeper into your driving experience and connects it to your real needs and desires.











Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.