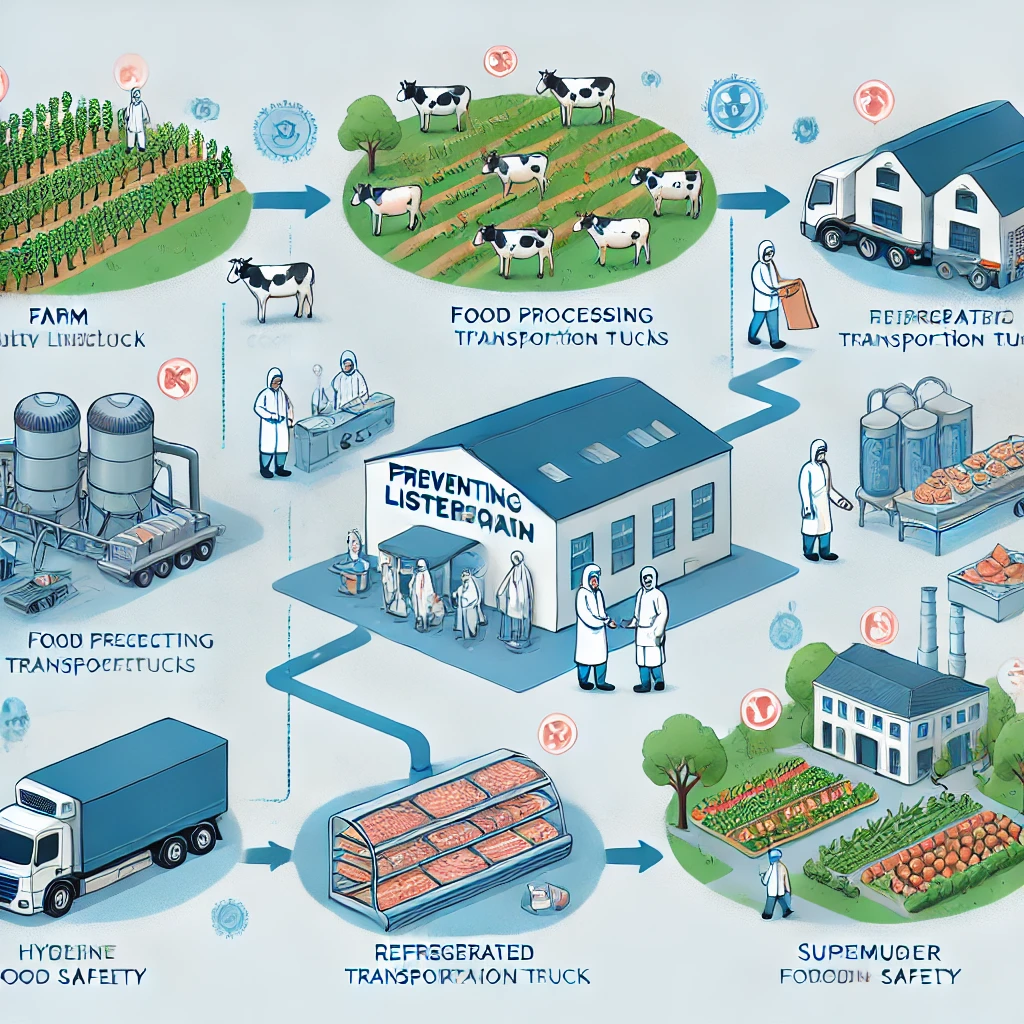
introduce
Lister’s disease, a serious foodborne disease Listeria monocytogenesposing a major threat to public health and food safety. This pathogen is particularly dangerous due to its ability to survive and reproduce in cold environments, which makes it persistently risky in food production and distribution. To ensure consumers’ safety, food industry stakeholders must take strict measures to prevent contamination at every stage of the supply chain, from farm to fork.
Also read: 10 Best Websites for Farmers to Sell Products
Understand Lister’s disease and its risks
Lister’s disease mainly affects people with weak immune systems, including pregnant women, newborns, elderly people and people with chronic diseases. Symptoms range from mild flu conditions to severe complications such as meningitis, septicemia, and even miscarriage in pregnant women. Given its serious consequences Prevent Lister’s disease It is crucial for food production and supply chain management.
Key points in the supply chain to prevent Lister’s disease
1. On the farm: Prevention starts at the source
The first line of defense in confrontation Listeria monocytogenes Starting from the agricultural phase. Precautions for farms include:
- Health practice: Ensure proper hygiene of livestock, fruits and vegetables can minimize the introduction of Listeria.
- Water quality control: Using clean, pathogen-free water for irrigation and animal hydration helps prevent contamination.
- Animal health monitoring: Infected animals can hide Listeriaregular inspection is required.
- Proper waste management: Eliminating rotten organic matter and fertilizers effectively reduces the risk of bacterial growth.
2. Food processing and manufacturing: Eliminate the risk of pollution
Food processing facilities are high-risk areas for Listeria contamination. Implementing strict sanitation and monitoring programs can mitigate risks:
- Hygiene design of facilities: Prevent the formation of biofilms (protective bacterial layers) by designing easy-to-clean surfaces and equipment.
- Strict temperature control: The refrigeration system must be well maintained because Listeria can grow at low temperatures.
- Staff training: Ensure workers follow hygiene protocols such as washing hands, wearing protective gear and maintaining sanitary workspaces.
- Frequent testing: Routine wipes and environmental monitoring to detect and eliminate potential sources of contamination.
3. Cold chain logistics: Ensure safe transportation
Listeria can thrive in cold environments, making temperature-controlled transport crucial in the supply chain.
- Maintain proper refrigeration: Transport vehicles must always keep the temperature below 4°C (39°F) to prevent bacterial growth.
- Prevent cross-pollution: Separating raw foods from ready-to-eat foods in transportation minimizes the risk of cross-contamination.
- Regular hygiene: Cleaning and disinfecting transport containers and vehicles reduces the chances of bacterial durability.
4. Retail and Food Services: Maintaining Food Safety Standards
Grocery stores, supermarkets and restaurants play a crucial role in preventing Listeria contamination before food attracts consumers.
- Appropriate storage conditions: Retailers should ensure that refrigerated products are kept at optimal temperatures and avoid expired products.
- Food treatment plan: Employees should be trained in safety treatment practices, including cleaning agricultural products, avoiding cross-contamination and proper sanitation.
- Regular inspections: Monitor food safety standards through routine inspections and compliance with health regulations.
5. Consumer awareness: The ultimate defense against Listeria
Despite major precautions taken by food industry professionals, food safety must also be educated to prevent the use of Lister’s disease at home.
- Proper refrigeration: Store decayable items at 4°C (39°F) or below slow down bacterial growth.
- Cook to a safe temperature: Cook raw meat, poultry and seafood to the recommended temperature eliminates harmful bacteria.
- Sanitary food treatment: Wash hands after handling raw food, tableware and surfaces will reduce the risk of contamination.
- Check the expiration date: Avoid expired or improperly stored food to minimize the possibility of consuming contaminated products.
Implementation of techniques in preventing listerobic disease
Advances in food safety technology have revolutionized the ability to detect and prevent Listeria Pollution in the supply chain.
- Real-time temperature monitoring: IoT-enabled sensors help ensure that decaying goods are stored and transported at safe temperatures.
- Rapid Pathogen Detection System: Modern testing methods can provide faster results, enabling early detection and response to contamination risks.
- Traceable blockchain: Enhanced transparency in the food supply chain allows for faster recall and improved tracking of contaminated products.
Regulatory compliance and industry standards
Governments and international food safety organizations have established strict guidelines to mitigate Listeria risks. Key regulations include:
- FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) (US): Authorized hazard analysis and prevention and control in food production.
- EU Food Safety Standards: Implement strict hygiene and monitoring programs for food safety.
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP): Systematic methods to identify and control food safety hazards.
in conclusion
Preventing Lister’s disease requires a comprehensive multi-layer approach throughout the supply chain. By implementing strict hygiene standards, maintaining proper temperature control, and leveraging modern technology, food producers, distributors, retailers and consumers can work together to minimize the risks associated with it. Listeria monocytogenes. Strengthening food safety from farm to fork is not only a necessity of regulation, but also a fundamental responsibility to protect public health and ensure consumers’ trust in the food industry.
(Tagstotranslate)Agricultural Industry (T)Global Logistics (T)Global Trade (T)Supply Chain (T)Supply Chain Management











Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.